Understanding Email Routing
Email routing is a crucial aspect of email communication that often goes unnoticed by the average email user. Essentially, email routing refers to the process of directing an email from its sender to its intended recipient. This process involves several steps and components that work together to ensure that the email reaches its destination accurately and efficiently.
When you hit the send button on your email client, the message doesn’t magically appear in the recipient’s inbox. Instead, it goes through a complex routing system involving different servers, protocols, and algorithms. Here’s a breakdown of some key elements of email routing:
SMTP Servers
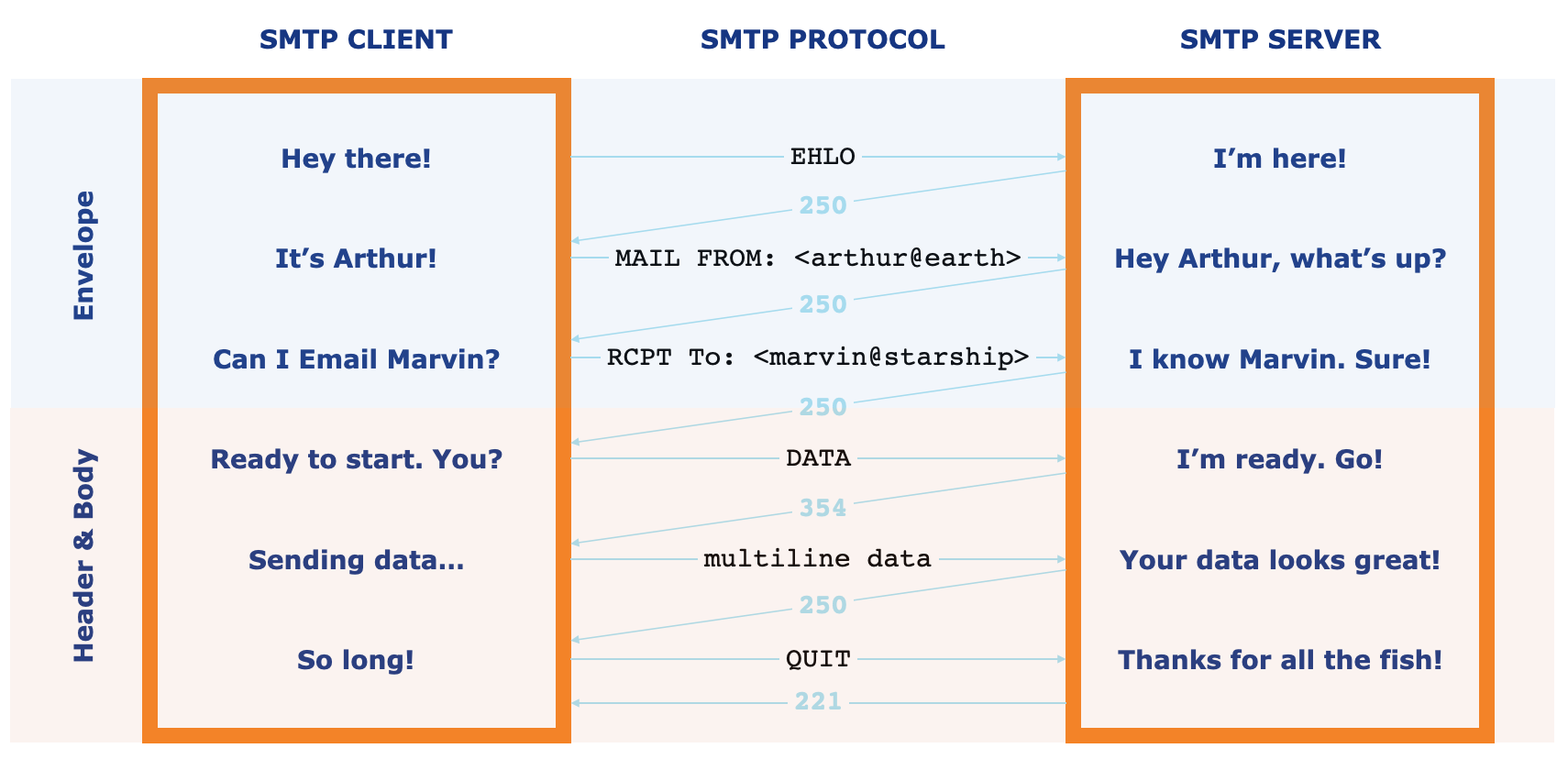
The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) servers play a vital role in email routing. These servers are responsible for sending, receiving, and relaying email messages between different email clients. When you send an email, your SMTP server communicates with the recipient’s SMTP server to transmit the message across the internet.
SMTP servers act as the post offices of the email world, ensuring that your messages are delivered to the right addresses securely and efficiently. They use a series of checks and validations to prevent spam, phishing, and other malicious activities.
DNS Records
Domain Name System (DNS) records are another crucial component of email routing. These records contain information about the domain names associated with email servers, which helps in routing emails to the correct destination. DNS records include MX (Mail Exchange) records that specify the servers responsible for receiving email on behalf of a domain.
When you send an email, your SMTP server consults the DNS records of the recipient’s domain to determine the appropriate destination server. This process ensures that the email is routed correctly, regardless of the recipient’s email provider.
Spam Filters
Spam filters are another critical component of email routing that helps in protecting users from unwanted and potentially harmful emails. These filters analyze incoming messages based on various criteria, such as sender reputation, content relevancy, and attachment types.
When an email passes through multiple servers during routing, spam filters examine its content and attachments to determine if it poses any security risks. If a message is flagged as spam, it may be redirected to the recipient’s spam folder or blocked entirely to prevent any potential threats.
Firewalls and Security Protocols
Firewalls and security protocols play a crucial role in email routing by protecting email servers and networks from external threats. These security measures monitor incoming and outgoing traffic for suspicious activities, such as malware, viruses, and unauthorized access attempts.
By implementing firewalls and security protocols, organizations can ensure that their email routing systems remain secure and resilient against cyberattacks. These measures help in safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining the integrity of email communications.
Delivery Reports and Tracking
Delivery reports and tracking mechanisms provide valuable insights into the status and progress of email routing. These features allow senders to monitor the delivery of their messages, track open rates, and analyze engagement metrics.
By leveraging delivery reports and tracking tools, organizations can optimize their email routing strategies, improve deliverability rates, and enhance overall communication efficiency. These insights help in identifying potential issues, resolving delivery problems, and enhancing the user experience for both senders and recipients.
In conclusion, email routing is a complex yet essential process that ensures the seamless transmission of messages across the digital landscape. By understanding the key components and mechanisms involved in email routing, users can better appreciate the reliability and efficiency of modern email communication systems.