How to Enable Automatic Security Updates on Red Hat
In today’s digital age, cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving and becoming more sophisticated. To protect your systems from these threats, it is crucial to ensure that security updates are applied in a timely manner. Red Hat, a leading provider of open-source solutions, offers a feature that allows you to enable automatic security updates on your Red Hat systems. This article will guide you through the process of enabling this feature and help you stay one step ahead of potential security vulnerabilities.
Step 1: Installing the yum-cron package
The first step to enabling automatic security updates on Red Hat is to install the yum-cron package. This package provides a simple way to configure automated updates for your system. To install the yum-cron package, open a terminal window and run the following command:
sudo yum install yum-cron
After the installation is complete, proceed to the next step.
Step 2: Configuring the yum-cron service
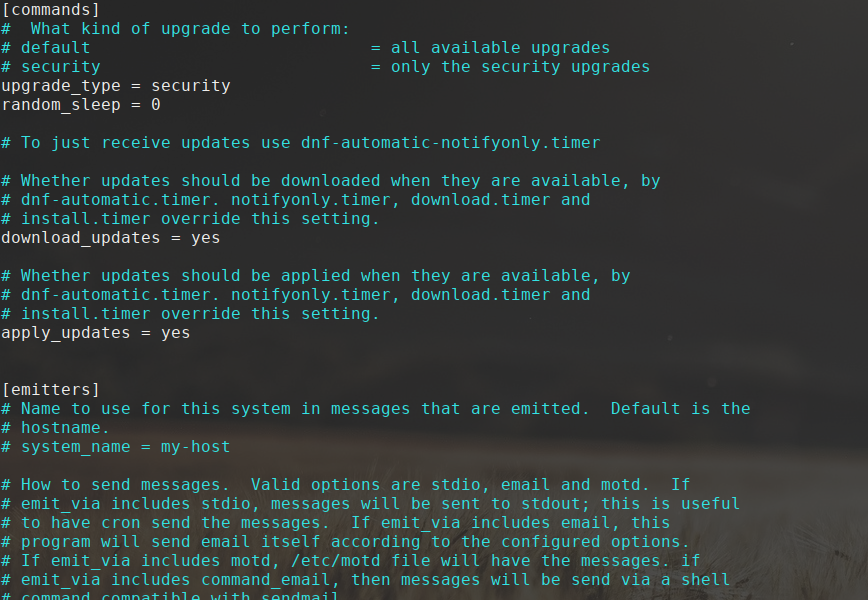
Once the yum-cron package is installed, you need to configure the yum-cron service to automatically apply security updates. To do this, open the /etc/yum/yum-cron.conf file in a text editor:
sudo nano /etc/yum/yum-cron.conf
In the yum-cron.conf file, locate the following line:
apply_updates = no
Change the value from no to yes to enable automatic updates:
apply_updates = yes
Save the changes and close the file.
Step 3: Starting the yum-cron service
After configuring the yum-cron service, you need to start the service to enable automatic security updates. To start the yum-cron service, run the following command:
sudo systemctl start yum-cron
The yum-cron service will now automatically check for and apply security updates on your Red Hat system. You can also enable the service to start automatically at system boot by running the following command:
sudo systemctl enable yum-cron
Step 4: Verifying automatic security updates
To verify that automatic security updates are working correctly, you can check the yum-cron log file. This log file contains information about the updates that have been applied to your system. To view the yum-cron log file, run the following command:
sudo cat /var/log/yum.log
If you see entries in the log file indicating that security updates have been successfully applied, then automatic security updates are working as expected.
Conclusion
Enabling automatic security updates on your Red Hat system is an essential step in ensuring the security and integrity of your systems. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can automate the process of applying security patches and stay protected from potential security vulnerabilities. Remember to regularly check the yum-cron log file to verify that automatic updates are being applied successfully. Stay vigilant and keep your systems secure!