How to Set Up SPF Records for Your Email Domain
Sending emails is a crucial aspect of communication in today’s digital world. However, sometimes emails sent from your domain may end up in the recipient’s spam folder. This happens when your domain lacks proper authentication, making it vulnerable to spoofing and phishing attacks. One way to prevent such issues is by setting up SPF records for your email domain.
SPF, which stands for Sender Policy Framework, is an email authentication protocol that helps verify the sender’s identity and prevent email spoofing. By creating SPF records for your domain, you authorize specific IP addresses and servers to send emails on your behalf, reducing the chances of your emails being marked as spam.
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to set up SPF records for your email domain:
Step 1: Access Your Domain’s DNS Settings
The first step is to log in to the control panel of your domain registrar and access your domain’s DNS settings. Look for the option to manage DNS records or edit DNS settings.
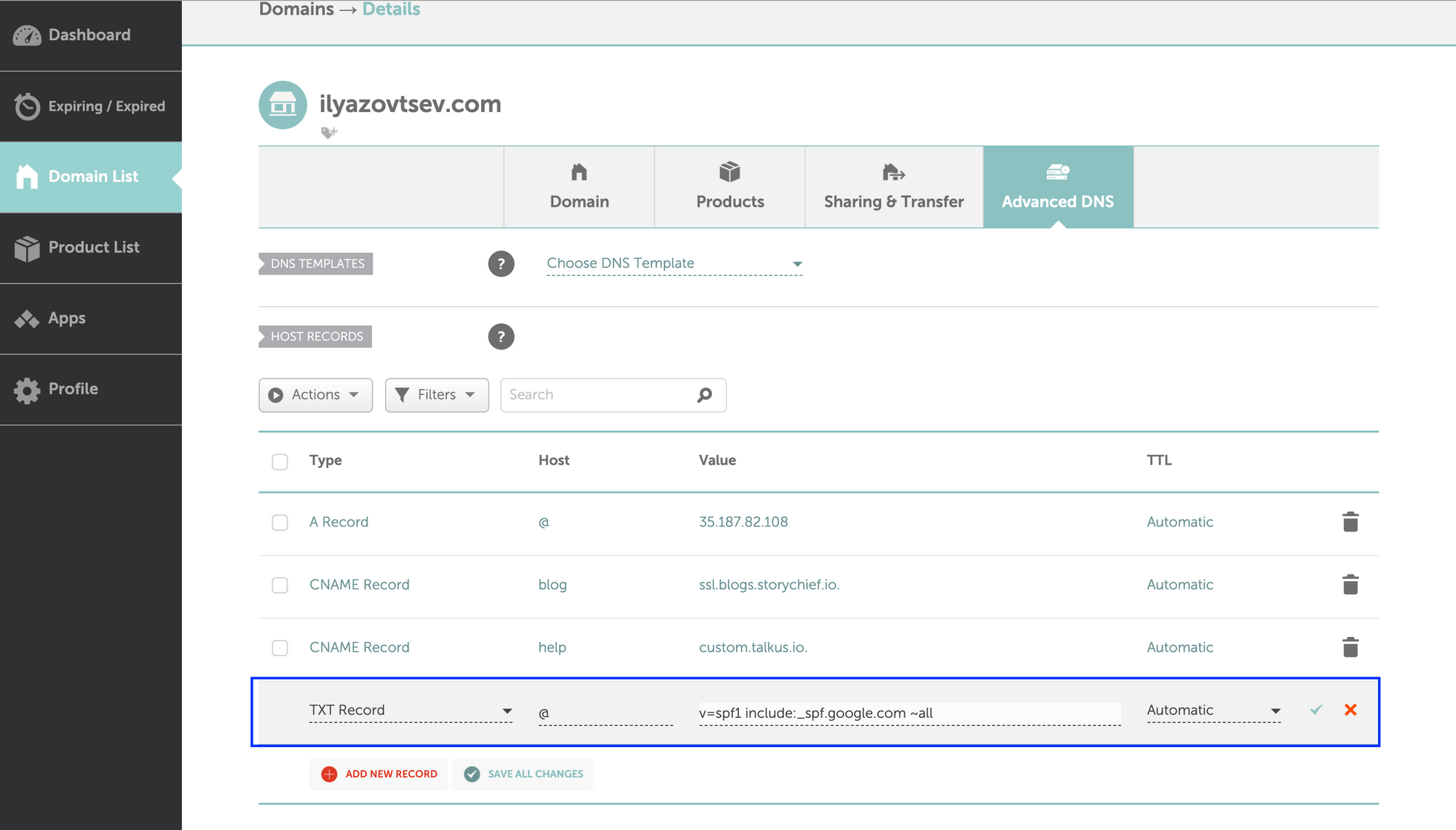
Step 2: Create a TXT Record for SPF
Once you’re in the DNS settings, locate the option to add a new DNS record. Choose the TXT record type and enter your SPF record in the provided field. The SPF record typically starts with “v=spf1” followed by the IP addresses or servers authorized to send emails on behalf of your domain.
For example, your SPF record may look like this:
v=spf1 ip4:192.0.2.0/24 include:emailprovider.com -all
In this example, the SPF record allows the IP address range 192.0.2.0/24 and the domain emailprovider.com to send emails on behalf of your domain. The “-all” tag at the end indicates a strict SPF policy, instructing receiving servers to reject emails that do not match the authorized criteria.
Step 3: Save the Changes and Verify the SPF Record
After entering the SPF record, save the changes in your DNS settings. To ensure the SPF record is properly configured, you can use online SPF record checkers to verify its syntax and validity.
It’s important to note that setting up SPF records is just one part of email authentication. To enhance the security of your domain, consider implementing additional measures such as DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance).
By following these steps and setting up SPF records for your email domain, you can improve the deliverability and credibility of your emails, ensuring that they reach the intended recipients without being flagged as spam.
Remember to regularly review and update your SPF records to reflect any changes in your email infrastructure and maintain the integrity of your domain’s email authentication.
With proper SPF records in place, you can enhance the security of your email communications and build trust with your recipients, ultimately benefiting your business or organization in the long run.