Understanding Domain or IP Address Port
When it comes to accessing websites or servers over the internet, you may have heard the terms “domain” and “IP address” being thrown around. But have you ever wondered what a port has to do with it? In this article, we will break down the concept of domain or IP address ports and why they are essential for connecting to online resources.
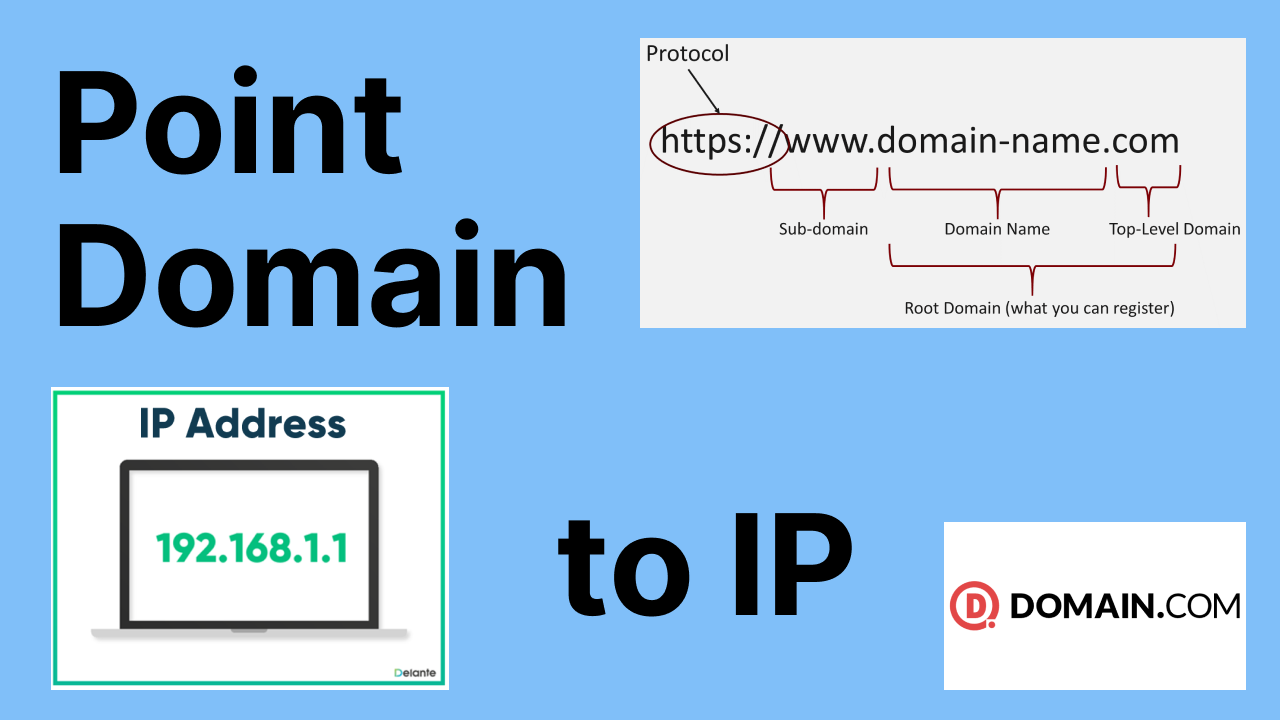
Let’s start with the basics. A domain is a user-friendly name used to identify a website or server on the internet. For example, “example.com” is a domain name. On the other hand, an IP address is a numerical label assigned to devices connected to a network. It serves as the actual address of a website or server on the internet.
Now, you may be wondering what a port is and how it relates to domains or IP addresses. In simple terms, a port is like a door that allows communication between devices over a network. Just like how shipping containers are loaded and unloaded through specific doors at a port, data is transferred through designated ports on a device.
Why Do We Need Ports?
Ports are essential for communication between devices on a network because they allow multiple services to run on the same device without interference. Each port is assigned a specific number, and different services use different ports to communicate with each other. For example, web servers typically use port 80 or 443 for HTTP and HTTPS communication.
When you type a domain name like “example.com” into your web browser, the browser translates it into an IP address using the Domain Name System (DNS). Once it has the IP address, it connects to the server using a specific port number. By default, web browsers use port 80 for HTTP and port 443 for HTTPS connections.
Similarly, when you access an email server or an FTP server, your device connects to specific ports on the server to send or receive data. Without ports, devices wouldn’t know where to send and receive data, making communication over a network impossible.
Common Port Numbers
While there are thousands of ports available for communication, some common port numbers are used for specific services:
- Port 21: FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
- Port 25: SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
- Port 53: DNS (Domain Name System)
- Port 80: HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
- Port 443: HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure)
- Port 3389: RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol)
Understanding port numbers is crucial for configuring firewalls, routers, and network devices to allow or block specific services. By knowing which port numbers are associated with different services, you can control the flow of data in and out of your network effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, domain or IP address ports play a vital role in how devices communicate over a network. Ports act as gateways that allow data to flow between devices, enabling services like web browsing, email, and file transfer to function smoothly. By understanding the concept of ports and their significance, you can ensure seamless communication between devices on the internet.