Domain Name vs IP
When it comes to navigating the vast world of the internet, domain names and IP addresses play a crucial role in connecting users with websites. Both domain names and IP addresses are essential components of the internet, but they serve different purposes and are used in different ways. In this article, we will explore the differences between domain names and IP addresses, and why both are important in the digital landscape.
What is a Domain Name?
A domain name is a human-readable address that serves as the online identity of a website. It is the familiar name that users type into their web browsers to access a specific website. Domain names are made up of two main components: the top-level domain (TLD) and the second-level domain (SLD). The TLD is the last part of the domain name, such as .com, .org, or .net, while the SLD is the main part of the domain name.
For example, in the domain name “example.com,” “example” is the SLD, and “.com” is the TLD. Domain names are registered through domain registrars, who are responsible for managing the registration and renewal process of domain names.
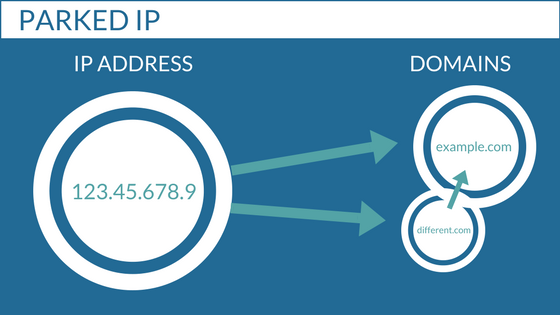
What is an IP Address?
An IP address, short for Internet Protocol address, is a numeric label assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. IP addresses serve as the unique identifier of a device on a network and are used to enable communication between devices.
There are two types of IP addresses: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 addresses consist of four sets of numbers separated by periods, such as 192.0.2.1, while IPv6 addresses are longer and more complex, such as 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334.
Domain Name vs IP Address
While domain names and IP addresses both serve the purpose of connecting users with websites, they are used in different ways. Domain names are user-friendly and easy to remember, making it convenient for users to access websites without having to memorize a string of numbers. On the other hand, IP addresses are essential for routing data packets across the internet and identifying devices on a network.
Domain names act as a human-readable alias for IP addresses, allowing users to type in a domain name instead of a string of numbers to access a website. When a user types in a domain name, the Domain Name System (DNS) translates the domain name into the corresponding IP address of the website, enabling the user to connect to the website’s server.
IP addresses, on the other hand, are used by routers and servers to route data packets across the internet. When a user types in a domain name, the DNS server looks up the corresponding IP address of the website and uses it to route the data packets to the correct destination. This process allows for seamless communication between devices on the internet.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both domain names and IP addresses are essential components of the internet that work together to enable communication between devices. Domain names provide a user-friendly way to access websites, while IP addresses serve as the unique identifier of devices on a network. Understanding the differences between domain names and IP addresses can help users navigate the internet more effectively and appreciate the complexity of the digital world we live in.