Domain Name vs Domain: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to navigating the world wide web, understanding the difference between a domain name and a domain is crucial. While these two terms may seem similar, they serve different purposes and are used in different contexts. In this article, we’ll explore the nuances of domain names and domains, and why they are important in the realm of website ownership and management.
What is a Domain Name?
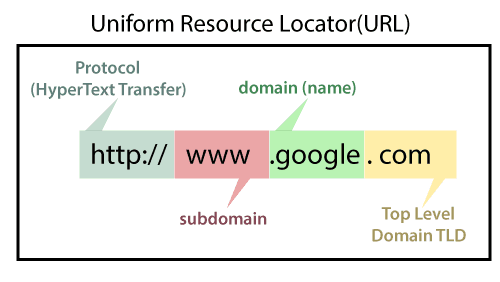
A domain name is the human-readable address of a website that people type into their browsers to access a specific website. For example, in the domain name “www.example.com,” “example.com” is the domain name. Domain names are used to identify and locate websites on the internet, making them crucial for online visibility and branding.
Domain names are made up of two main parts: the top-level domain (TLD) and the second-level domain (SLD). The top-level domain is the last part of the domain name, such as .com, .org, .net, .edu, etc. The second-level domain is the part that comes before the TLD, and it is usually the unique name chosen by the website owner.
Domain names are registered through domain registrars, who are responsible for managing the domain registration process and ensuring that domain names are unique and functional. When you register a domain name, you are essentially claiming ownership of that specific web address, allowing you to build a website and establish an online presence.
What is a Domain?
On the other hand, a domain refers to a broader internet address space that encompasses multiple domain names. Domains are hierarchical in nature, with the most specific domain names being on the left and the most general domain names on the right. For example, in the domain “www.example.com,” “.com” is the top-level domain, “example” is the second-level domain, and “www” is a subdomain.
Domains are managed by organizations called domain registries, which are responsible for maintaining the domain name system (DNS) and ensuring that domain names are properly translated into IP addresses. The DNS is like the internet’s phone book, translating human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses so that computers can communicate with each other.
Key Differences
- Domain names are specific web addresses that people type into browsers, while domains encompass multiple domain names.
- Domain names are registered through domain registrars, while domains are managed by domain registries.
- Domain names consist of a top-level domain and a second-level domain, while domains are hierarchical internet address spaces.
Understanding the difference between a domain name and a domain is essential for anyone looking to establish a website or online presence. By grasping the nuances of these terms, you can navigate the world of web addresses with confidence and clarity.
Whether you’re registering a new domain name or managing an existing domain, having a solid understanding of these concepts will help you make informed decisions about your online presence. So, the next time you’re deciding on a domain name or configuring your website’s domain settings, remember the distinction between a domain name and a domain.