Domain name vs DNS: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to navigating the world wide web, two terms that often come up are domain name and DNS. While these concepts may seem similar, they actually serve different purposes in the world of websites and online services. In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between domain names and DNS, and why they are both essential for running a successful online presence.
Domain Name
A domain name is the unique address that users type into their browsers to access a particular website. It is like the street address of a house, helping users navigate the internet and find the content they are looking for. Domain names are typically composed of a series of letters, numbers, and symbols, with different extensions like .com, .org, .net, and more. For example, google.com and amazon.com are both domain names that point to the websites of the companies.
Domain names are purchased from domain registrars, who manage the registration process and ensure that each domain name is unique. When a user types a domain name into their browser, the internet’s DNS (Domain Name System) translates that domain name into an IP address, which is the actual location of the website’s servers. This process allows users to access websites using human-readable names instead of complex numerical IP addresses.
DNS
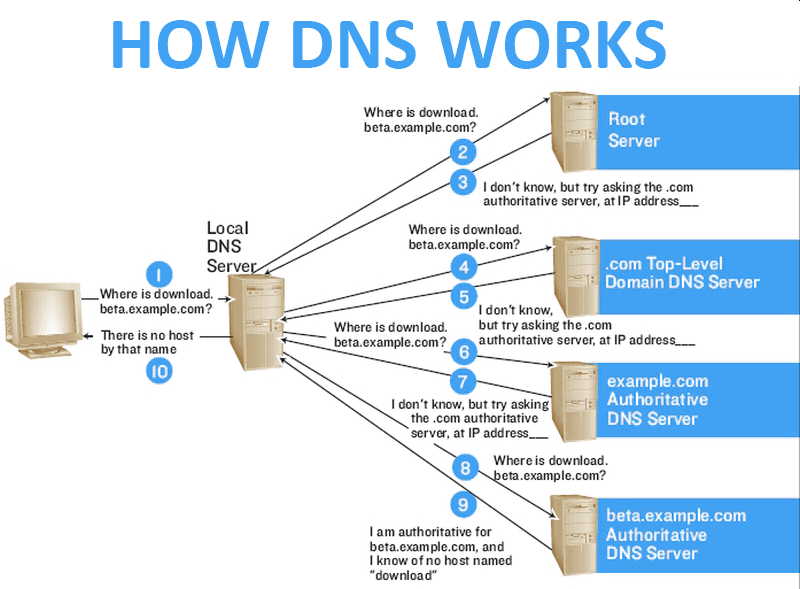
DNS, short for Domain Name System, is like the internet’s phone book. It is a hierarchical and decentralized system that translates domain names into IP addresses, allowing users to access websites and online services. DNS servers store information about domain names and their corresponding IP addresses, making the internet more user-friendly and accessible.
When a user types a domain name into their browser, the DNS servers are queried to find the corresponding IP address of the website’s servers. This process involves multiple DNS servers working together to retrieve the correct information and deliver it to the user’s browser. Without DNS, users would have to remember complex IP addresses to access websites, which would make browsing the internet much more challenging.
Key Differences
- Domain names are human-readable addresses for websites, while DNS translates these names into IP addresses.
- Domain names are purchased from domain registrars, while DNS servers are a network of servers that translate domain names into IP addresses.
- Domain names are essential for branding and marketing, while DNS is essential for the technical functioning of the internet.
In conclusion, domain names and DNS are both crucial components of the internet ecosystem. While domain names serve as the address for websites, DNS ensures that users can access these websites seamlessly. Understanding the differences between domain names and DNS can help website owners and internet users navigate the online world more effectively and make informed decisions about their online presence.