Domain Controller IP Address Best Practice
Choosing the right IP address for your domain controller is crucial to ensure smooth operation and security of your network. In this article, we will discuss some best practices to consider when assigning IP addresses to your domain controllers.
Domain controllers are the backbone of your Active Directory infrastructure. They store information about user accounts, computers, group policies, and more. Therefore, it is important to properly manage their IP addresses to avoid any issues.
Static vs. Dynamic IP Address
One of the first decisions to make when assigning IP addresses to domain controllers is whether to use static or dynamic IP addresses. While dynamic IP addresses are easier to manage, static IP addresses are recommended for domain controllers as they provide stability and ensure that the server always has the same IP address.
By using a static IP address, you can avoid issues such as IP conflicts and ensure that other servers and devices on the network can always reach the domain controller at the same address.
Subnetting
When planning the IP address scheme for your domain controllers, consider subnetting to improve network performance and security. Subnetting involves dividing your network into smaller, more manageable subnets, which can help reduce network congestion and improve security by isolating different parts of the network.
Assigning separate subnets for domain controllers can also help in better organizing your network and simplifying troubleshooting in case of any network issues.
Private IP Address Range
It is best practice to use private IP addresses from the designated range for internal networks, such as 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255, 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255, or 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255. These ranges are reserved for private networks and are not routable over the internet, ensuring the security of your network.
Using public IP addresses for domain controllers can expose them to security risks and potential attacks. Therefore, always stick to using private IP addresses for your internal network.
DNS Settings
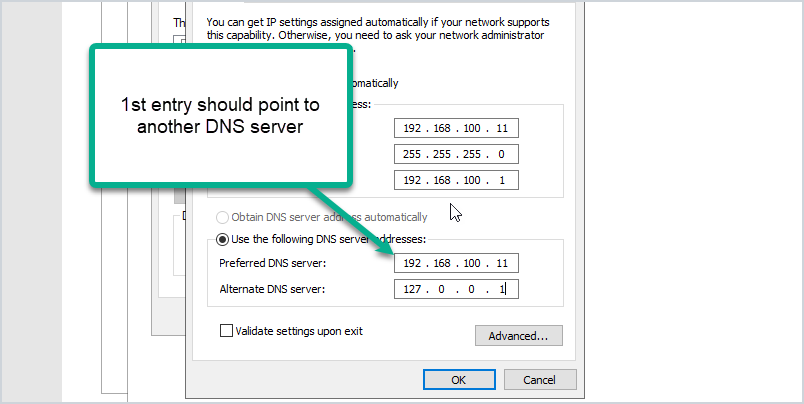
Proper DNS configuration is essential for domain controllers to function correctly. When assigning IP addresses to domain controllers, ensure that they have correct DNS settings, including primary and secondary DNS servers.
Verify that the domain controllers themselves are pointing to the correct DNS servers, and make sure that the DNS servers have forward and reverse lookup zones properly configured to resolve hostnames and IP addresses.
Firewall Rules
When assigning IP addresses to domain controllers, it is important to configure firewall rules to allow necessary traffic to and from the domain controllers. This includes enabling communication with other domain controllers, DNS servers, and client computers on the network.
Restricting unnecessary traffic and opening only the required ports can help in improving the security of your network and preventing unauthorized access to the domain controllers.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring and maintenance of domain controllers’ IP addresses are essential to ensure the ongoing stability and security of your network. Keep track of IP address changes, monitor network traffic, and perform regular security audits to identify any potential vulnerabilities.
Document the IP addresses assigned to each domain controller and keep the documentation up to date to quickly identify any issues or changes in the network.
Conclusion
Assigning the right IP addresses to domain controllers is crucial for the security and stability of your network. By following best practices such as using static IP addresses, subnetting, using private IP address ranges, configuring proper DNS settings, setting up firewall rules, and regular monitoring, you can ensure that your domain controllers operate efficiently and securely.
Remember, proper IP address management is key to a well-functioning Active Directory infrastructure.