DNS Records for Mail: Everything You Need to Know
When it comes to setting up email communication for your domain, understanding DNS records for mail is crucial. These records are essential in directing your email traffic to the right mail server, ensuring that your emails are delivered successfully. In this article, we will discuss the different types of DNS records related to email, their functions, and how to configure them properly.
Types of DNS Records for Mail
There are several DNS records that are commonly used for managing email delivery. The primary records include:
- MX (Mail Exchange) Records
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework) Records
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) Records
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) Records
MX (Mail Exchange) Records
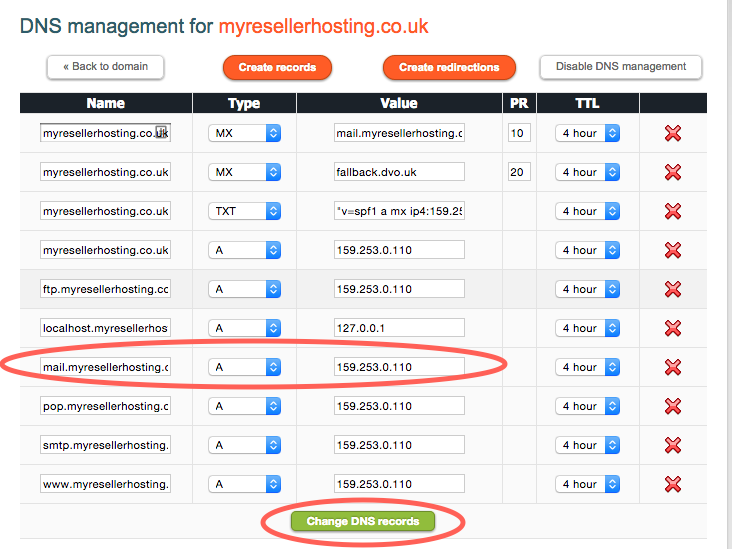
MX records are used to specify the mail servers that should receive email messages addressed to a specific domain. Each MX record has a priority value, which determines the order in which mail servers should be used. It is essential to configure MX records correctly to ensure proper email delivery.
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) Records
SPF records are designed to prevent email spoofing by listing the IP addresses that are authorized to send emails on behalf of a domain. By configuring SPF records, you can specify which servers are allowed to send emails using your domain name, thereby reducing the likelihood of your emails being marked as spam.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) Records
DKIM records add a digital signature to outgoing email messages, allowing the recipient’s email server to verify that the message was not altered during transmission. By implementing DKIM records, you can enhance the security and trustworthiness of your email communications.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) Records
DMARC records provide instructions to email servers on how to handle emails that fail SPF and DKIM checks. By setting up DMARC records, you can specify whether to deliver, quarantine, or reject emails that do not pass authentication checks. This helps protect your domain from email spoofing and phishing attacks.
How to Configure DNS Records for Mail
Configuring DNS records for mail involves accessing your domain’s DNS settings and adding or modifying the necessary records. Most domain registrars provide user-friendly interfaces for managing DNS records. Here are the general steps to configure DNS records for mail:
- Access your domain registrar’s control panel or DNS management tool.
- Locate the section for managing DNS records.
- Add MX records to specify your mail servers.
- Configure SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records for enhanced email security.
- Save your changes and allow some time for the DNS changes to propagate.
It is recommended to regularly monitor and update your DNS records to ensure that your email communications remain secure and reliable.
Conclusion
Setting up and maintaining proper DNS records for mail is essential for ensuring the security and reliability of your email communications. By understanding the functions of MX, SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records, you can effectively manage your email delivery and protect your domain from email spoofing and phishing attacks. Remember to regularly review and update your DNS records to stay ahead of potential email security threats.