AWS EC2 Charges for Stopped Instances
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a leading cloud service provider that offers a wide range of services to businesses and individuals. One of the services offered by AWS is the Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), which allows users to launch virtual servers in the cloud. While EC2 is a powerful tool for scaling your infrastructure, it’s essential to understand how AWS charges for stopped instances to avoid unexpected costs.
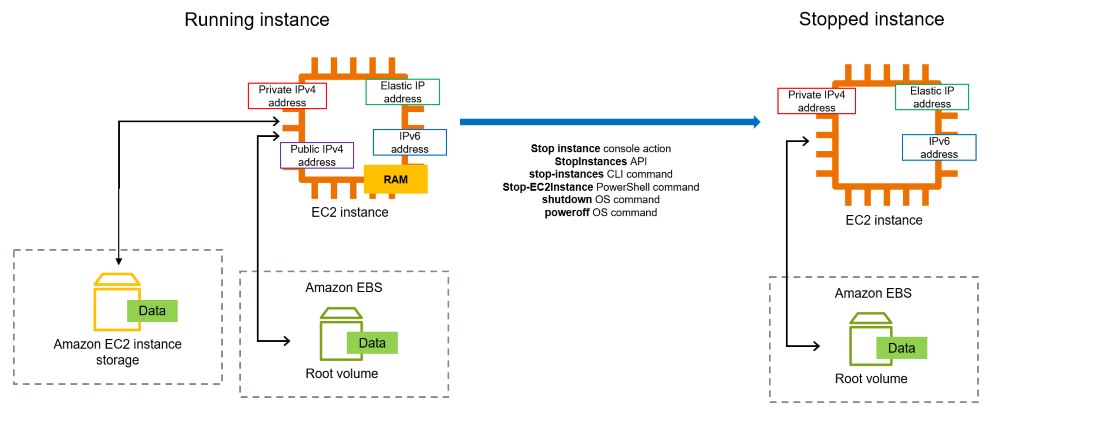
When you stop an EC2 instance in AWS, the instance is still stored in the cloud, and you continue to incur charges for the associated EBS storage. AWS charges for stopped instances because the underlying resources, such as storage and data transfer, are still allocated to the instance, even if it’s not running.
It’s crucial to monitor your AWS usage regularly to ensure that you’re not accruing unnecessary charges for stopped instances. By understanding how AWS bills for EC2 instances, you can optimize your usage and avoid unexpected costs.
How AWS Charges for Stopped Instances
When you stop an EC2 instance in AWS, you’re only stopping the instance itself, not the associated resources like EBS volumes. AWS continues to charge for the EBS storage used by the stopped instance, as well as any other associated resources like Elastic IP addresses or data transfer fees.
It’s essential to understand how AWS charges for stopped instances to avoid unexpected costs. By monitoring your usage and optimizing your resource allocation, you can ensure that you’re only paying for the resources you actually need. This can help you save money on your AWS bill and improve the efficiency of your infrastructure.
Why AWS Charges for Stopped Instances
AWS charges for stopped instances because the underlying resources are still allocated to the instance, even when it’s not running. This includes storage, data transfer, Elastic IP addresses, and any other resources associated with the instance. By charging for stopped instances, AWS encourages users to optimize their resource usage and only allocate the resources they actually need.
While it may seem unfair to be charged for resources you’re not actively using, it’s important to remember that AWS is a pay-as-you-go service. By understanding how AWS charges for stopped instances and monitoring your usage, you can minimize unnecessary costs and make the most of your AWS resources.
Optimizing Your AWS Usage
To optimize your AWS usage and minimize costs, it’s essential to monitor your EC2 instances regularly. Make sure to terminate any instances you no longer need and remove any unused resources to avoid unnecessary charges.
Consider using AWS Cost Explorer to analyze your usage patterns and identify areas where you can save money. By taking proactive steps to optimize your AWS usage, you can ensure that you’re only paying for the resources you actually need and avoid unexpected costs for stopped instances.
Conclusion
Understanding how AWS charges for stopped instances is crucial for managing your AWS costs effectively. By monitoring your EC2 usage, optimizing your resource allocation, and taking proactive steps to minimize costs, you can ensure that you’re getting the most value out of your AWS resources.
Remember to regularly review your AWS bill, analyze your usage patterns, and make adjustments as needed to avoid unexpected charges and optimize your infrastructure. By following best practices for managing your AWS usage, you can save money and improve the efficiency of your cloud infrastructure.