Add DMARC Record for Office 365
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) is a protocol that helps prevent email phishing and spoofing attacks. By implementing a DMARC record for your Office 365 domain, you can protect your organization’s email reputation and ensure that legitimate emails are delivered to recipients’ inboxes.
Adding a DMARC record for Office 365 is a straightforward process that involves updating your domain’s DNS settings. In this article, we will guide you through the steps to create and add a DMARC record to your Office 365 domain.
Step 1: Understand DMARC
Before creating a DMARC record, it’s essential to understand how it works. A DMARC record specifies the policy for email authentication and specifies what actions should be taken for emails that fail authentication checks. The record also includes information on where to send DMARC reports for analysis.
DMARC works in conjunction with SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) to authenticate email messages. By implementing these technologies, you can verify the authenticity of incoming emails and prevent phishing attacks.
Step 2: Create a DMARC Record
To create a DMARC record for your Office 365 domain, you will need to generate the DMARC policy and add it to your DNS records. The DMARC policy consists of three main components: the policy type, the domain name, and the enforcement policy.
- Policy Type: Specifies how the email should be handled if it fails authentication.
- Domain Name: Specifies the domain for which the DMARC policy is in effect.
- Enforcement Policy: Specifies whether to monitor, quarantine, or reject emails that fail authentication.
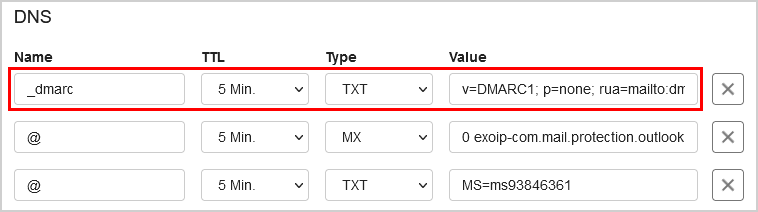
Here’s an example of a DMARC record that you can use for your Office 365 domain:
v=DMARC1; p=none; pct=100; rua=mailto: [email protected]
Step 3: Add the DMARC Record to Office 365
To add the DMARC record to your Office 365 domain, you will need to access your DNS settings. Depending on your DNS provider, the exact steps may vary. Generally, you will need to log in to your DNS provider’s website, locate the DNS settings for your domain, and add a new TXT record with the DMARC policy.
Once the DMARC record has been added to your DNS settings, it may take some time for the changes to propagate. You can use online tools to verify the DMARC record and ensure that it has been set up correctly.
Step 4: Monitor DMARC Reports
After adding the DMARC record to your Office 365 domain, it’s essential to monitor the DMARC reports to identify any issues with email authentication. DMARC reports provide detailed information on the email authentication results, including the number of emails that pass or fail authentication checks.
By analyzing the DMARC reports, you can identify potential phishing attacks and take corrective action to protect your organization’s email reputation. Regularly reviewing the reports will help ensure that your DMARC policy is effectively preventing unauthorized emails from reaching your recipients.
Implementing a DMARC record for Office 365 is a crucial step in securing your organization’s email communications. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can enhance the security of your email infrastructure and protect your organization from phishing attacks.