Domain Name vs Hostname
When it comes to navigating the world of the internet, it’s essential to understand the difference between a domain name and a hostname. These terms may seem similar, but they serve different functions in the world of web addressing. In this article, we will break down the differences between domain names and hostnames to help you navigate the digital landscape with ease.
What is a Domain Name?
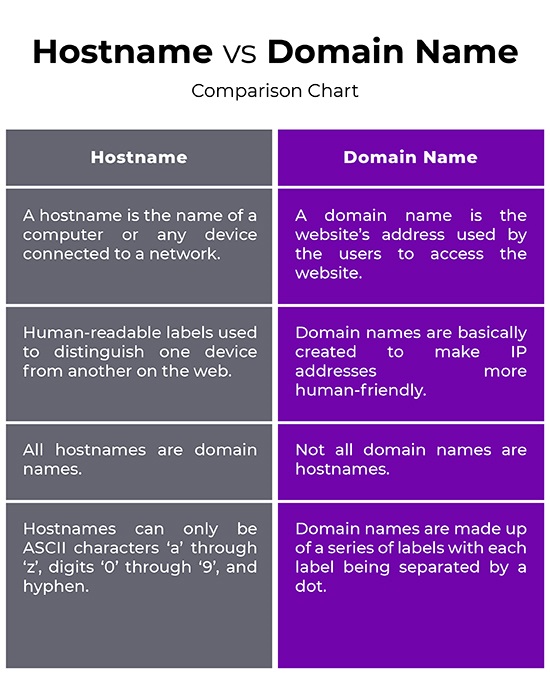
A domain name is the human-readable address that you type into your web browser to visit a website. It is a unique and easy-to-remember name that represents an IP address. Domain names are hierarchical, with the top-level domain (TLD) at the end (such as .com, .org, .net) and the second-level domain (SLD) preceding it (such as google.com, apple.com). Domain names are purchased from domain registrars and must be renewed periodically to maintain ownership.
What is a Hostname?
A hostname, on the other hand, is a label assigned to a device connected to a network. It can refer to a computer, server, router, or any other device that communicates over a network. Hostnames are used within the networking infrastructure to identify devices and manage traffic efficiently. Unlike domain names, hostnames are not necessarily human-readable and are used for internal network communication.
Key Differences
- Function: Domain names represent web addresses that users type into their browsers. Hostnames identify devices within a network for communication purposes.
- Human-Readability: Domain names are designed to be easily readable by humans. Hostnames may not be as user-friendly.
- Ownership: Domain names are purchased from registrars and must be renewed. Hostnames are assigned to devices by network administrators and do not require renewal.
Example Scenario
Let’s imagine you want to visit the website “example.com.” In this case, “example.com” is the domain name that you type into your browser. Behind the scenes, the website is hosted on a server with its unique IP address, which is identified by a hostname such as “webserver01.” The domain name “example.com” points to the IP address associated with the hostname “webserver01,” allowing users to access the website seamlessly.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between domain names and hostnames is crucial for navigating the internet effectively. While domain names act as user-friendly addresses for websites, hostnames help identify devices within a network. By grasping the distinctions between these two terms, you can enhance your knowledge of web addressing and connectivity in the digital realm.
Next time you type a domain name into your browser, remember the behind-the-scenes work of hostnames that make it all possible!