Understanding Domain Controller IP Address
Domain controllers are a crucial component of any network infrastructure, responsible for authenticating and authorizing all users and computers in a domain network. One important aspect to consider when setting up a domain controller is the IP address configuration. In this article, we will delve into the importance of domain controller IP addresses and how to ensure they are properly configured.
What is a Domain Controller?
A domain controller is a server that responds to security authentication requests within a Windows Server domain. It manages network security services, including user authentication, enforcing security policies, and distributing software across a network domain. Without a domain controller, users would not be able to log into their accounts, access shared resources, or perform other network-related tasks.
Importance of Domain Controller IP Address
The IP address of a domain controller is essential for its proper functioning within a network. The IP address allows other devices on the network to locate and communicate with the domain controller. It is crucial to assign a static IP address to the domain controller to ensure its stability and ease of access.
Configuring Domain Controller IP Address
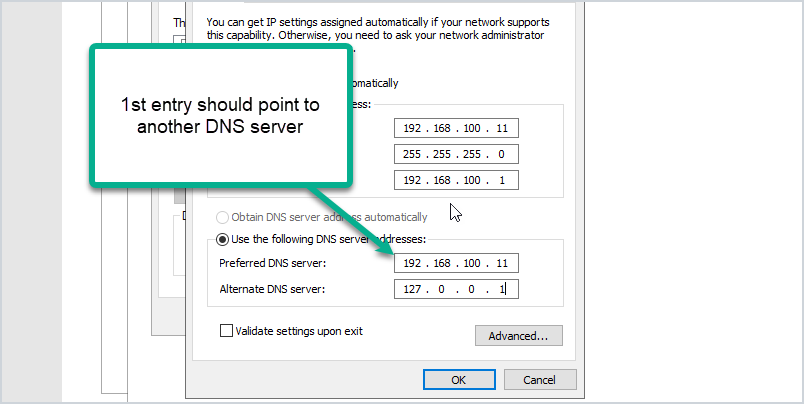
When setting up a domain controller, you must configure its IP address to ensure seamless communication within the network. Follow these steps to configure the domain controller’s IP address:
- Open the Control Panel and navigate to Network and Sharing Center.
- Click on Change adapter settings.
- Right-click on the network adapter and select Properties.
- Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click on Properties.
- Choose “Use the following IP address” and enter the desired IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway.
- Click OK to save the changes.
After configuring the domain controller’s IP address, ensure that all other devices on the network can communicate with it. Verify the connectivity by pinging the domain controller’s IP address from another device on the network. If the ping is successful, the domain controller’s IP address is correctly configured.
Best Practices for Domain Controller IP Address
Here are some best practices to follow when configuring a domain controller’s IP address:
- Assign a static IP address to the domain controller to prevent network disruptions.
- Ensure the IP address is within the same subnet as other devices on the network.
- Configure backup DNS servers to ensure continuous network connectivity.
- Regularly monitor and update the domain controller’s IP address settings for any changes.
By following these best practices, you can ensure the stability and reliability of your domain controller’s IP address, contributing to a secure and efficient network infrastructure.
Conclusion
Domain controller IP address configuration is a critical aspect of network management. By properly configuring and managing the IP address of a domain controller, you can ensure seamless communication within the network and maintain network security. Remember to follow best practices and regularly monitor the IP address settings to keep your domain controller functioning optimally.